Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
Whatsapp
-
E-mail
The significance of printing machines in modern industries cannot be overstated, as they have evolved into indispensable tools that facilitate a wide range of applications. According to a report by Smithers Pira, the global printing industry was valued at approximately $400 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach around $500 billion by 2026. This growth can be attributed to the increasing demand for customized printing solutions across various sectors, including packaging, textiles, and commercial printing. Printing machine innovations, such as digital and 3D printing technologies, have further driven this expansion, enabling businesses to enhance productivity and reduce waste.
In industrial manufacturing, the printing machine plays a crucial role in streamlining operations. For instance, the packaging industry extensively utilizes advanced printing machines to produce vibrant, high-quality labels and packaging materials that meet consumer demands. Reports indicate that the demand for printed packaging is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.6% between 2021 and 2026. Furthermore, the textile industry has witnessed a surge in the adoption of digital printing machines, with the global market expected to reach $4 billion by 2025, due in large part to the growing trend of fast fashion and need for rapid prototyping.
Overall, the multifaceted applications of printing machines across various industries highlight their integral role in driving innovation and efficiency, ultimately sustaining the growth of the global economy. Understanding how printing machines work and their varying applications can provide valuable insights for businesses looking to optimize their operational capabilities.
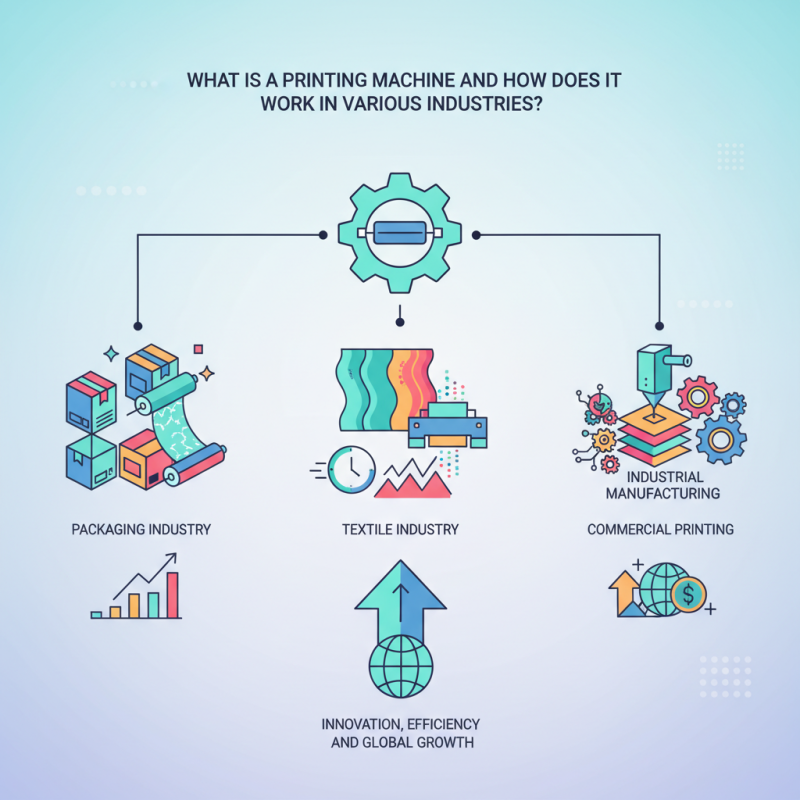
Printing machines are essential tools used across diverse industries for producing images, text, and designs on various materials. Understanding the types of printing machines available is crucial for selecting the right one for specific applications. The most common types include offset printing, flexography, digital printing, and screen printing. Each method employs unique techniques to transfer ink onto substrates, catering to different requirements such as print quality, speed, and volume.
In the publishing industry, offset printing is favored for its high-quality output and efficiency in large-scale production. Flexography is widely used in packaging, as it can print on a variety of surfaces, including plastic and foil, making it ideal for labeling and flexible packaging. Digital printing has gained popularity in recent years due to its versatility and ability to produce short runs quickly, making it suited for custom prints and on-demand production. Screen printing offers vibrant colors and is best for textiles and promotional items, allowing for detailed designs on fabric or metal surfaces. Each type of printing machine plays a vital role in meeting industry demands, influencing how products are manufactured and marketed.
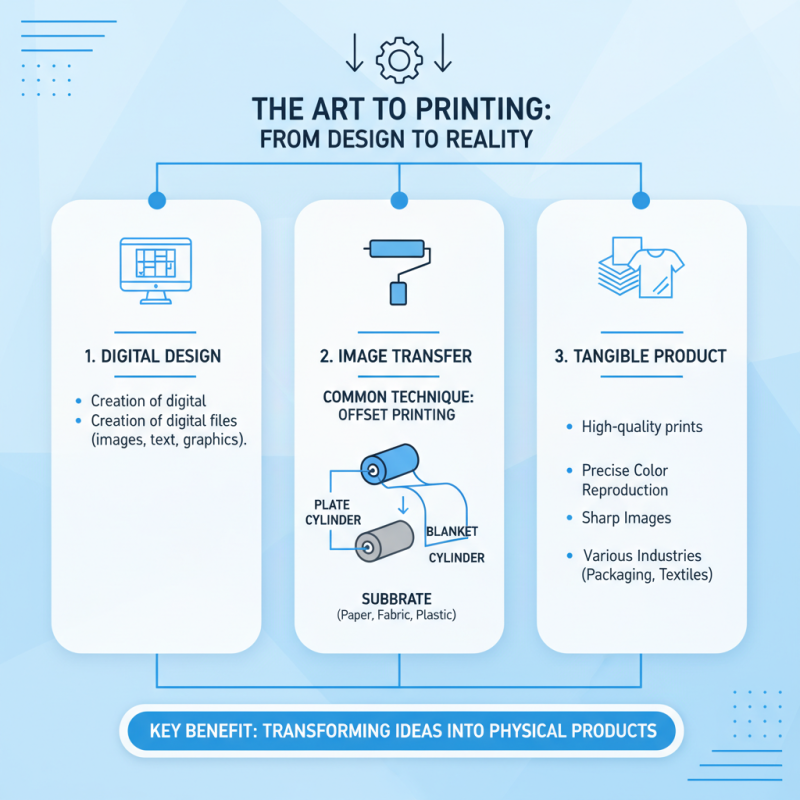
Printing machines are intricate devices that transform digital designs into tangible products across various industries. The mechanism of printing fundamentally begins with the image transfer process, where inks or toners are applied onto a substrate—be it paper, fabric, or plastic—through specialized methods. One of the most common techniques is offset printing, where an intermediary surface carries the ink before applying it to the final material. This ensures high-quality prints with precise color reproduction and sharp images.
In the digital era, digital printing has gained prominence due to its efficiency and flexibility. Unlike traditional methods, digital printers bypass the need for physical plates, allowing for quick setup and shorter print runs. This not only saves time but also reduces waste, making it a favored choice for many businesses needing customization and rapid turnaround.
Tips: When choosing a printing method, consider the scale and nature of your project. For large volumes, offset printing may be more cost-effective, while digital printing excels in personalized short runs. Additionally, always test your colors with proofs to ensure accuracy and satisfaction before the full run.
Printing machines play a crucial role in various industries, driving efficiency and innovation across the board. In the packaging sector, for instance, the global print packaging market was valued at approximately $400 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach around $500 billion by 2027, according to a recent market report. This growth can be attributed to the increasing demand for sustainable and visually appealing packaging solutions. Digital printing technologies have transformed this industry, enabling businesses to produce customized packaging at reduced costs and shorter turnaround times, allowing for greater flexibility in meeting consumer needs.
In the textile industry, printing machines have revolutionized the way fabrics are designed and produced. The global digital textile printing market is projected to grow from $2.5 billion in 2022 to over $5 billion by 2027, primarily driven by advancements in ink technologies and the rising demand for personalized fashion items. Techniques such as sublimation and direct-to-garment (DTG) printing not only enhance production speed but also reduce waste, aligning with the increasing consumer preference for environmentally friendly practices. Whether for home textiles, fashion apparel, or promotional materials, the adaptability of printing machines has solidified their importance across diverse applications within this dynamic industry.
In recent years, innovations in printing technology have significantly transformed various industries, driving productivity and efficiency to new heights. Advancements such as digital printing, 3D printing, and eco-friendly ink formulations have revolutionized traditional manufacturing processes. For instance, digital printing allows for quicker turnaround times and greater customization, enabling businesses to respond more adeptly to market demands. Meanwhile, 3D printing is not just reshaping manufacturing but is also opening new avenues for design and prototyping, making it easier and more cost-effective to produce complex parts.
Tips: When considering adopting new printing technologies, evaluate your specific needs carefully. Understand how these innovations can align with your production goals. Additionally, ensure that your workforce is adequately trained to work with the latest printing equipment, as this can greatly enhance operational efficiency.
The impact of these innovations extends beyond just speed and efficiency; they also contribute to sustainability. Many modern printing machines are designed to reduce waste and energy consumption, addressing environmental concerns while meeting production needs. Techniques such as on-demand printing minimize excess inventory, allowing for a more agile and responsive production cycle.
Tips: Consider exploring environmentally sustainable options when selecting printing machines. Opting for printers that use less energy and sustainable materials not only benefits the planet but can also improve your brand's image in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
The future of printing machines is set to be defined by technological advancements and shifting industry demands. According to a report by Smithers Pira, the market for digital printing is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% through 2024. This aligns with the increasing need for customization and shorter print runs across various industries, leading to a greater reliance on digital technologies, which allow for faster turnaround times and reduced waste. As traditional offset printing faces decline, innovations in inkjet and laser technologies promise to revolutionize how businesses approach their printing needs.
Moreover, the rise of sustainability practices in printing is likely to influence future developments significantly. A study by the Printing Industries of America highlights that 67% of print buyers prefer working with environmentally responsible companies. In response, many printing manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly materials and processes, integrating renewable energy sources and reducing carbon footprints. This shift not only meets consumer demand but also aligns with global efforts toward sustainability. As the industry evolves, the adaptation towards more sustainable and efficient printing solutions will be crucial for maintaining competitiveness and meeting regulatory standards in an increasingly environmentally-conscious market.
| Industry | Type of Printing Machine | Primary Function | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging | Flexographic Printer | Prints on flexible materials such as plastic, paper, and aluminum foil. | Increased automation and eco-friendly inks. |
| Textiles | Digital Textile Printer | Directly prints on fabric, allowing for intricate designs. | Sustainability and reduced water usage in printing processes. |
| Publishing | Offset Lithography | Used for high-volume book and magazine printing. | Integration of digital technologies for on-demand printing. |
| Advertising | Large Format Printer | Produces large-scale prints for banners and posters. | Expansion of 3D printing for signage and display. |
| Electronics | Screen Printer | Used for printing circuits on electronic components. | Development of flexible and printed electronics. |